.jpg)
Mobile App Development Lifecycle 2021
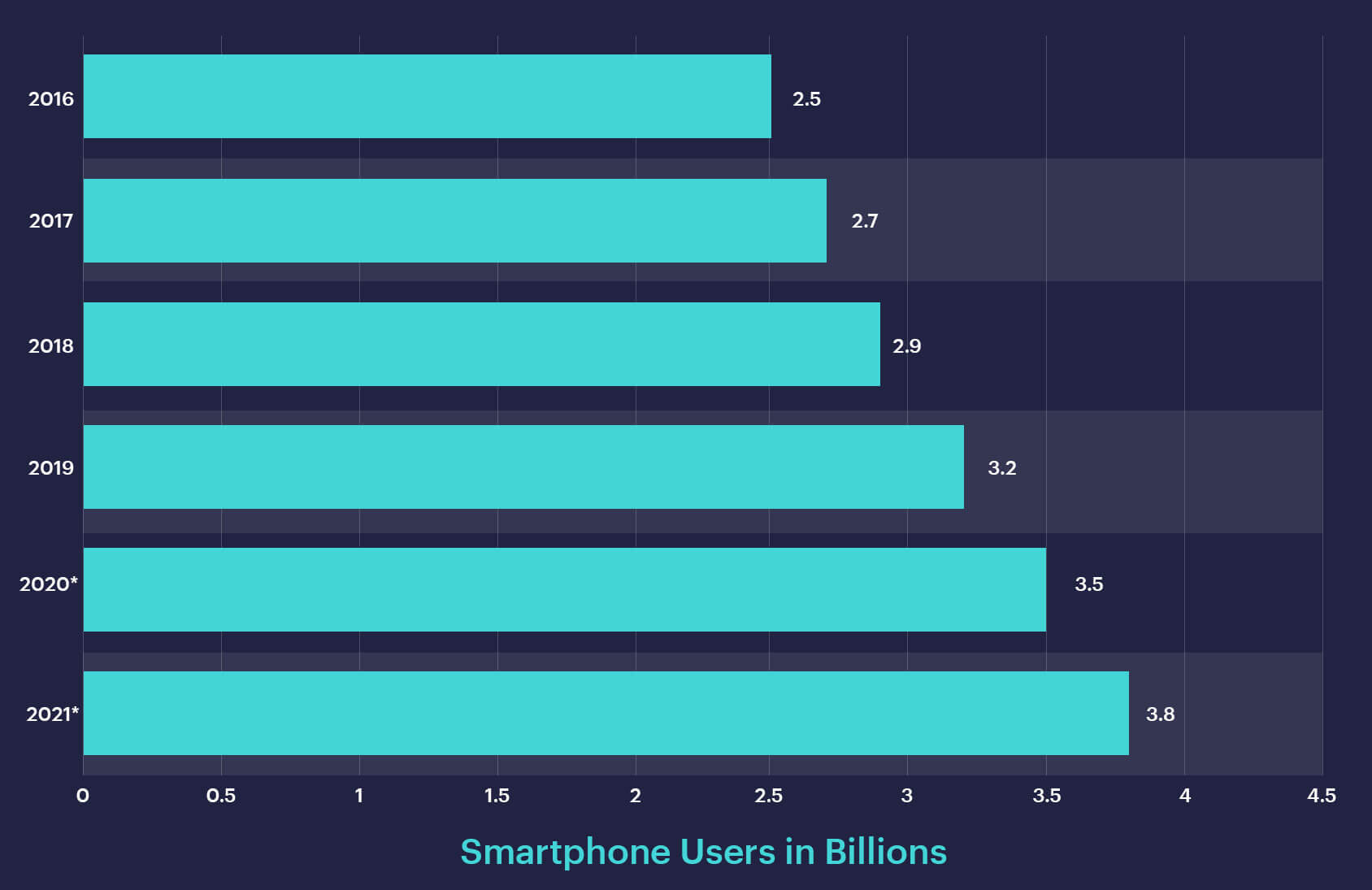
There are over 3.5 billion smartphone users worldwide, so there is no doubt that the industry is healthy and thriving. Stats are growing steadily, without any indications of slowing down. And studies show that an average American checks their phone at least once every twelve minutes, and over 10% of these people check their phone about every four minutes. There are some more statistics to keep in mind.People spend over half of the time they spend with digital media on mobile.
Smartphone users spend 90% of their screen-on time using mobile apps.
Over 85% of consumers prefer native apps over mobile cross websites.
Revenue from mobile apps is set to cross $693 billion in 2021.
The average consumer has over 30 apps installed on their device.
An average user spends about 35 hours per month using mobile apps.
The statistics are motivating for anyone who wishes to build or develop a mobile app. But before we jump to any conclusions, let’s understand the exact process for mobile app development. Although it sounds very lucrative to build a mobile app to get a piece of the billion-dollar pie, the decision needs thought strategy and planning. The fact also states that your app will be competing with over 1.5 million applications on the Google Play Store and Apple’s App Store.
What is Mobile App Development?
Mobile app development is a process for building mobile applications that run on mobile devices. These applications can either be pre-installed or downloaded and installed by the user later. They use the network capabilities of the device to work computing resources remotely. Hence, the mobile app development process requires creating software that can be installed on the device, and enabling backend services for data access through APIs, and testing the application on target devices.
To develop scalable mobile apps, you also need to consider screen sizes, hardware requirements, and many other aspects of the app development process. With an increasing number of jobs in the mobile app development industry, it is essential that the process is well defined and understood by entrepreneurs, startups, and especially developers.
Mobile App Development Platforms
The two most important mobile app platforms are iOS from Apple Inc. and Android from Google. iOS is Apple’s proprietary mobile operating system built specifically for iPhones. Android, however, runs on mobile devices manufactured by various OEMs, including Google.
While there are many similarities between the two, however different software development kits (SDKs) are used for different platforms. Apple uses iOS exclusively for their own devices, while Google has made Android available for other companies that meet specific requirements. Developers have built over 1.5 million applications for both platforms to date.
Alternatives for Developing Mobile Apps
You can approach mobile app development in four different ways:Build Native Mobile Applications
Build Cross-Platform Native Mobile Applications
Build Hybrid Mobile Applications
Build Progressive Web Applications
There are advantages and disadvantages to building an application, no matter which approach you choose. By choosing an approach that matches your strategy, you can achieve the desired user experience, avail computing resources, and build native features required for your application.
Comparison of App Development Alternatives
Native Apps Cross-Platform Apps Hybrid Apps Progressive web Apps
Native applications are built using the tools and SDKs offered by platform owners like Apple and Google. These apps run natively on the platform of your choice. Cross-platform mobile applications can be written on various programming languages and then compiled for each platform separately. Hybrid Applications are built using the latest web technologies like JavaScript, CSS, HTML, and then bundled as mobile applications for the required platforms. Hybrid Apps are different from Cross-Platform Apps in the sense that they work using web containers using browser runtime. Progressive Web Apps don’t require native or cross-platform development. They skip the app store installations and also traditional app delivery channels. They work inside the browser, whether it be mobile or desktop. A link is added to the mobile in the form of an app icon. These are basically web applications that also run on mobile.
Native apps offer the best runtime performance. Single code base for multiple platforms. Codebase is shared between web and mobile apps. Apps run on the web, as well as mobile.
Directly use the platform’s data through platform-specific SDKs. A unified user experience can be offered even for different platforms. Web development tools can be used to build mobile applications. No need to install the app. Runs through a browser on URL using the network connection.
The cost of building and maintaining different codes for each platform is high. Since native libraries are not available, the dependency is on third-party open-source libraries. The performance is not native, as essentially, they are built using technologies for web development. Little or no support for native devices. Runs using browser’s capabilities.
Features have to be implemented differently based on the platform’s SDK tools. The code is not written natively. Thus, it has to be complied with and bridged. Which can be bugging. Little or no support for native devices. If the network connection is not available, interactivity is lost to a great extent.
Why Choose Native App Development?
Choosing native app development helps when you want to use native capabilities offered by the platform. Native apps can access the hardware capabilities of the devices like GPS, camera, microphone, which helps in quicker execution of features making it easier to build a rich user experience.
Push notifications are much easier to implement on native development. For example, push notifications to go through iOS Server (APNS) and Google’s Cloud Messaging Platform. Native apps have fewer bugs, as the code is compiled in the native language.
Why Choose Cross-Platform App Development?
The market is divided about 50-50 between iOS and Android. Your potential customer could be on any of the platforms, and sometimes on both. Building separate apps for both platforms requires an adequate budget, and not all companies have that. Moreover, developing native platforms can make it harder to offer the same amount of speed and functionality required by your app.
Choose cross-platform development if you wish to align the user experience across all the platforms; you wish to have one development team publishing for both the platforms; and you don’t have the budget and time to build and maintain two different apps separately.
Why Choose Progressive Web App Development?
Progressive Web Applications (PWAs) are written in traditional web languages like Javascript, HTML5, CSS, and such. These apps are only accessible through the browser of your device. So, choose to develop a PWA if your user will have uninterrupted access to network connectivity, and they can solve their issues through the browser itself, without requiring any native capabilities of the device like camera, machine learning module, GPS, gyroscope, and such.
With that in mind, let’s understand the mobile app development process step by step and get to know everything you need to follow a systematic mobile app development process to build your next great app.
Further Reading → Top Mobile App Development Software 2021
Mobile App Development Process
To build an application, you need a step-by-step process that can help you build mobile apps quickly. There are three important steps:Understand the requirement
Develop the Product
Test the product.
Build an App Development Strategy
The first step in the mobile app development process is to create a strategy by defining why? What is the objective of your app? How will your mobile app solve an industry problem? What is your business model? How much are you ready to invest in building this app? What is your revenue model? How will you market your app, and to who? Answering these questions will give you a fair idea of how you can move forward with your mobile app development process.
You can start by defining the user persona. For example, suppose you are planning to build an eCommerce app. In that case, you will define your user persona by understanding your user’s age, their mobile usage habits, their preference, and specifically answering why and how they will find your mobile app users. Based on this, you can create an MVP (Minimum Viable Product).
Read Further, How MVP help a Business in Developing Mobile Applications?
To build an effective strategy, you will have to do some of the following things:
Brainstorm your app idea
Building a mobile app starts with an app idea. However, you require an extensive amount of brainstorming to develop an ultimate list of features you can offer your customers. You can start with the essential elements and note down other lesser crucial features as they are revealed to you. Who knows, you might surprise yourself with ideas you never knew you could implement. Sit together with your team, and ask them for all the ideas they can come up with.
Market Research, Mobile App Development Tech Stack
Before you start, here are some questions you can ask yourself:Who is your target audience?
How will your customers use the application?
Are there any better alternatives already available?
What will your application do that other application won’t?
What business model are your customers following?
What language, frameworks, and technologies will you use?
How many uses are paying for your type of mobile application?
What is your budget?
How long will it take to build your application?
Define your Minimum Viable Product
Once you are clear about all the functionalities you can include, the functionalities your users will like to use from the start, you define what your minimum viable product would look like. A minimum viable product is the version of your app that has enough features to put it in front of your early customers so that you can receive feedback on product features and further development.
You build a minimum viable product for the following reasons:Test the product market using minimum resources
Get investors to see the vision behind your app
Quickly learn what works and what doesn’t
Waste minimum engineering hours
Get the product in front of early customers fast
Use it as a base to build other products
Test developer’s ability to build and scale product
Key elements of a minimum viable product (MVP)Functionality – offer clear value to the users
Design-build minimal but highest quality standard design
Reliability – make the production quality top notch
Usability – make the user experience intuitive and refined
Further reading: How much does it cost to build an app?
With a clear strategy in mind, you will be able to focus on your app development idea. Building a mobile app development strategy will help you analyze and plan your progress.
Analyse and Plan your App Development
The strategy is the starting point of all project development. Now, once you have a strategy in hand, start turning those visions into achievable goals. Start the analysis and planning by clearly defining how you can use the functionalities to build use cases and meanwhile, create a list of functional requirements.
This will help you build a product roadmap. You will be able to convert that strategy into a step by step process that you can turn into priorities, and then group them into delivery milestones. You must also have your minimum viable product defined, which will help you cut down on costs, and prepare for the initial launch.
Different operating systems require different technology stacks. Choose your tech stack based on your requirements. Whether you are building a native mobile application, a cross-platform mobile app, or a hybrid application, you will need to make a list of technologies required, and start hiring developers with expertise in your chosen mode of mobile app development.
Plus, you will need to finalize a name for your mobile application. To find the perfect name, you might want to contemplate your application’s features, differentiate the name using wordplay, keep it short and easily memorably, searchable, and probably an action word. Many app developers also go with obvious names, and sometimes they differ by trying to connect with consumers’ opinions. You should also keep in mind the process of App Store Optimization, which is important if you want to be found by users searching for apps similar to yours.
Build UX/UI Design
How your mobile application looks and feels makes a great deal of impression on the minds of your users. Whether it be a full-fledged application of an MVP, you have to make sure that the design is top-notch and that it offers the highest level of user experience. Designing mobile apps requires the understanding of the two important concepts of design: User experience and user interface.
What is User Experience Design?
User experience is what customers feel when they use your products. In our case, the design should be such that it creates a specific emotional response from the customer after using the app. User experiences include factors like design, accessibility, marketing, usability, system performance, ergonomics, HCI, and also utility. With an increasing number of companies focusing on user-centered design, creating an intuitive user experience for your mobile application is a no-brainer.
Further Reading → Mobile User Experience Design
What is User Interface Design?
Designers make sure that the mobile application looks crips and pleasurable. User Interface Design is the process of making your app look perfect, following the latest design trends, so that it complements the user experience. Designers often use principles like the structure principle, the simplicity principle, the visibility principle, the feedback principle, the tolerance principle, the reuse principle, and more.
Further reading → User Interface Design Principles / How to create mobile user interface design
Mobile App Design Process
Designing is much more than learning how to use design software. You can learn to design your mobile application yourself or ask someone to help you. But above everything else, the design is about understanding the product inside out, and its capabilities, features, and functionalities. The design should always keep the end-user in mind. The design process we follow at OpenXcell is as follows.Building User Flow / Diagram for each screen
Creating Wireframes
Choosing Design patterns, palettes, and elements
Creating mockups
Creating an animated prototype and asking testable questions
Give final touches to the mockup based on user feedback
Further reading → Simplified Mobile App Design Process
Wireframes
Most designers start by making rough sketches on paper. To simplify, wireframes are digital sketches, done using a wireframing tool, which you can also do using pen and paper. Wireframes are concepts, not finished designs. They simply help you understand the visual structure of your app’s features using low-fidelity mockups.
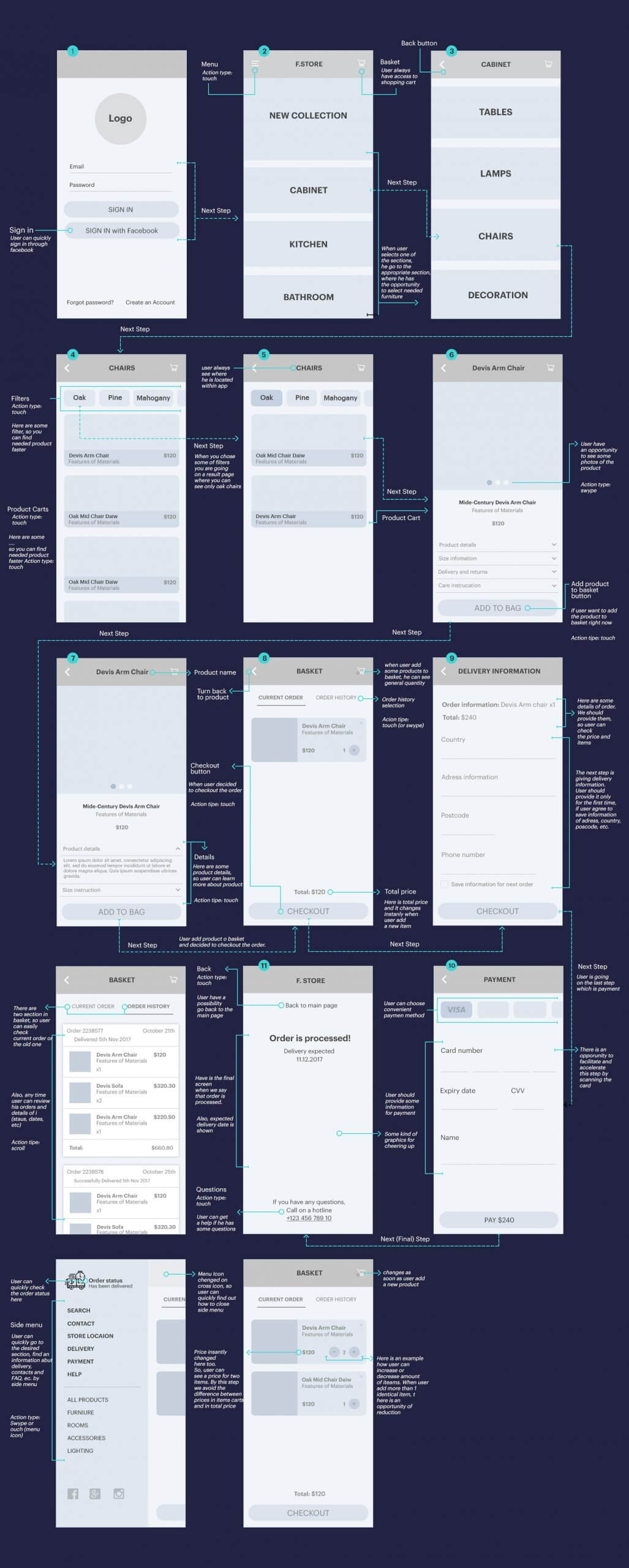
When you are designing wireframes, the focus has to be made on aesthetics and how the user will experience it. Color palettes and design elements are not required now. Wireframes are used to quickly understand what you want to be designed. It is important that you design that is specific to the product. No matter which device you are on, it should be intuitive and user-friendly.
Further Reading → How to build good wireframes
Style Guides
A style guide is a set of rules for the design. User interfaces can get tricky. Wireframes can be misunderstood. But if you have a style guide, your mobile app UI designer will understand what fonts have to be used, what color palette has been chosen, which icons are to be placed where, and many other important questions they might ask before designing.
Style guides create a base for the process of long-term evolution, switching design and development between parties, developing for differences in the platform. It also helps in sharing topics. Some of the elements you can consider for mobile app style guides are as follows:Fonts
Colors
Layouts
Graphics
Components
Menus and Bars
Dialogs and Alerts
Further reading → App Design style guides Example
Mockups
Eventually, you will move past the prototype phase, and build the final version of your mobile app development. These designs are called mockups, or high-fidelity designs. Mockups combine the wireframe and the style guide to build the final version, which can be sent for prototyping. You will expect further modifications in the structure, workflow, and even aesthetics at this stage to make it look and feel exactly like you want it to.
Some of the popular tools for building mockups are Figma, Sketch, Photoshop, and Adobe XD.
Prototype
Wireframes are good. But you will need interactivity to test the features so that you can receive feedback. Prototyping is about turning low-fidelity wireframes into ready designs that can be shared with your teams, friends, and everyone who can use it to offer their quality suggestions and feedback.
Most teams use products like InvisionApp to prototype their app. However, some companies also use Xcode to prototype their apps directly into the development environment.
Prototyping is essential if you are looking to pitch your app to investors. You can include all the functionalities without going through development. For testers, it helps by offering a real feel for what it would be like to use the application.
Further reading → Mobile App Prototyping Guide
Begin App Development
There are three important aspects of app development:Technical architecture
Technology stack
Development milestones
Most of mobile app development projects have three integral parts:Mobile Backend server technologies
Application Programming Interface (APIs)
Frontend development
What is Mobile App Backend Development?

What your users will see is the front end. The development that is required from the side of the server is the backend. Mobile app backends are used to store, secure, and process data. It refers to the activities that will happen behind the scenes when a user is interacting with your mobile application. Developing a backend for your mobile is used for sending information for processing on the server. Signups, logins, messaging, storing data on the cloud, answering user queries, and such other things happen in the backend.
Backend development focuses on storing information in a remote database, scripting to add logic to the interactivity, and creating architecture that makes it quick and easy to sort through the information.
Applications like a calculator, camera, notes, compass, voice recorder, and such don’t require a backend development. They run on the mobile app without any network connectivity, or the requirement to store or retrieve data from a remote server. However, apps like Amazon, Netflix, and Uber can’t run without a connected backend.
Further Reading → Everything you need to know about mobile app backend
Application Programming Interface (APIs) Development
Mobile apps have evolved into a state where they are constantly communicating with servers. Very few applications operate without connectivity, which means they use the backend, web service, or APIs. These APIs could be provided by companies like Amazon, Google, Facebook, or others, or developed internally by the mobile app development teams.
Most of the mobile API Development is done using RestAPI, which is also one of the simplest choices for anyone building mobile apps. It helps users quickly interact and connect with a remote cloud data server. However, making requests through the network can create major problems if not done right. Some things to take care of when building mobile APIs are:
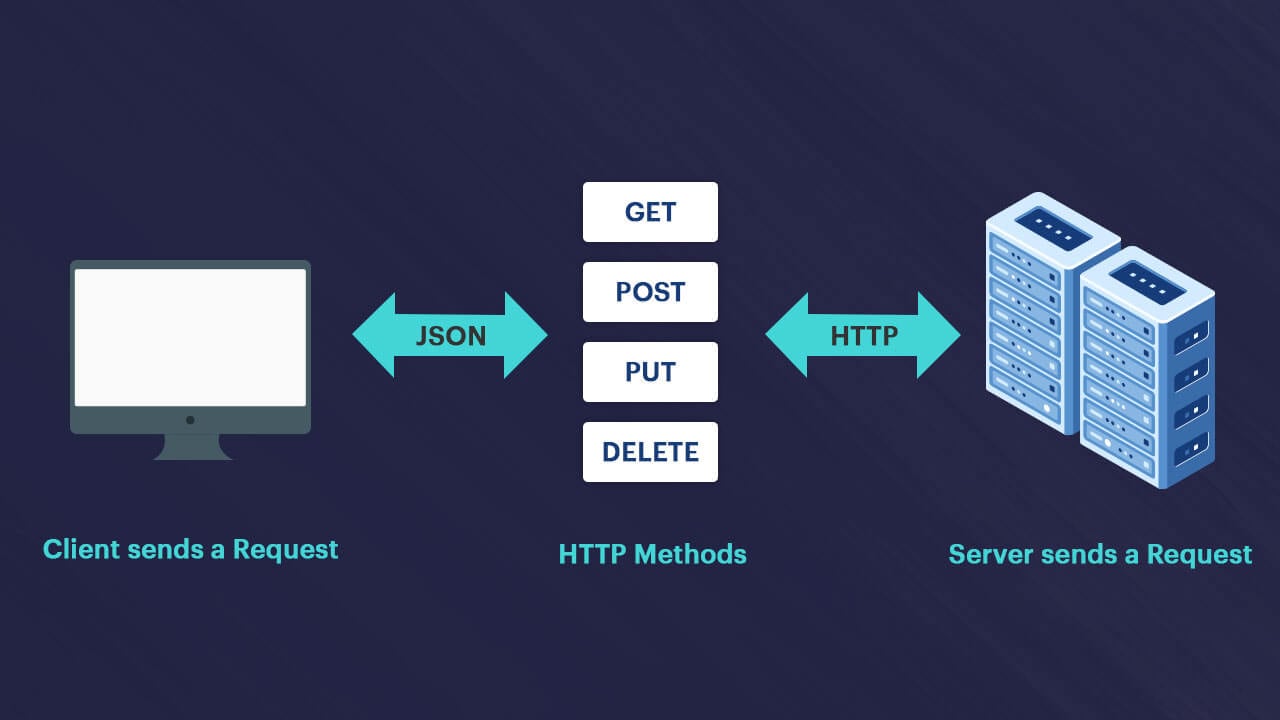
Understand how web services work. There is a wide variety of APIs available, however, most of them are based on REST, which returns data in JSON format.
Understand how HTTP protocols work. REST relies on HTTP protocols to handle data, so it is important to get familiar with the workings of HTTP URLs, the process of data transfer, and how it handles remote actions.
It is also important to learn how REST maps URLs to make the required requests.
Should you buy or build APIs?
There are two ways to integrate APIs to your mobile application. You can either build it yourself or you can buy from an existing API provider.
Purchasing a ready API and integrating it is the easiest because it saves time and money in the sense that you don’t need a developer to understand and implement API integration for you. However, building your own API gives you much more freedom and allows you to include or exclude features as per your requirement.
Before assembling a team and building your own custom API, it is better to explore the available options. Instead of reinventing the wheel, simply use what is already available even if that comes at a cost of saving your time to help you reach the market faster.
Using Common Architecture
When and if you decide to build your own API, it is best to go with a common architecture. It offers a general baseline for development which most developers are used to developing. This speeds up your mobile API development process. There are four different types of common architecture, which include pragmatic REST, web services, event-driven, and hypermedia. For mobile app development, the most preferred common architectures are pragmatic REST and event-driven.
Documenting the Mobile API Development Process
Developing an API is easy. However, teams evolve, and there is always going to be someone new looking at your code. Having a clear API process documentation can help you see the history, as well as the current state of API. This makes future updates easier. Another benefit of documenting your API development process is that it allows others to use your API. If you want other developers to use your API, you will need solid documentation to help you with the code.
Focusing on Security
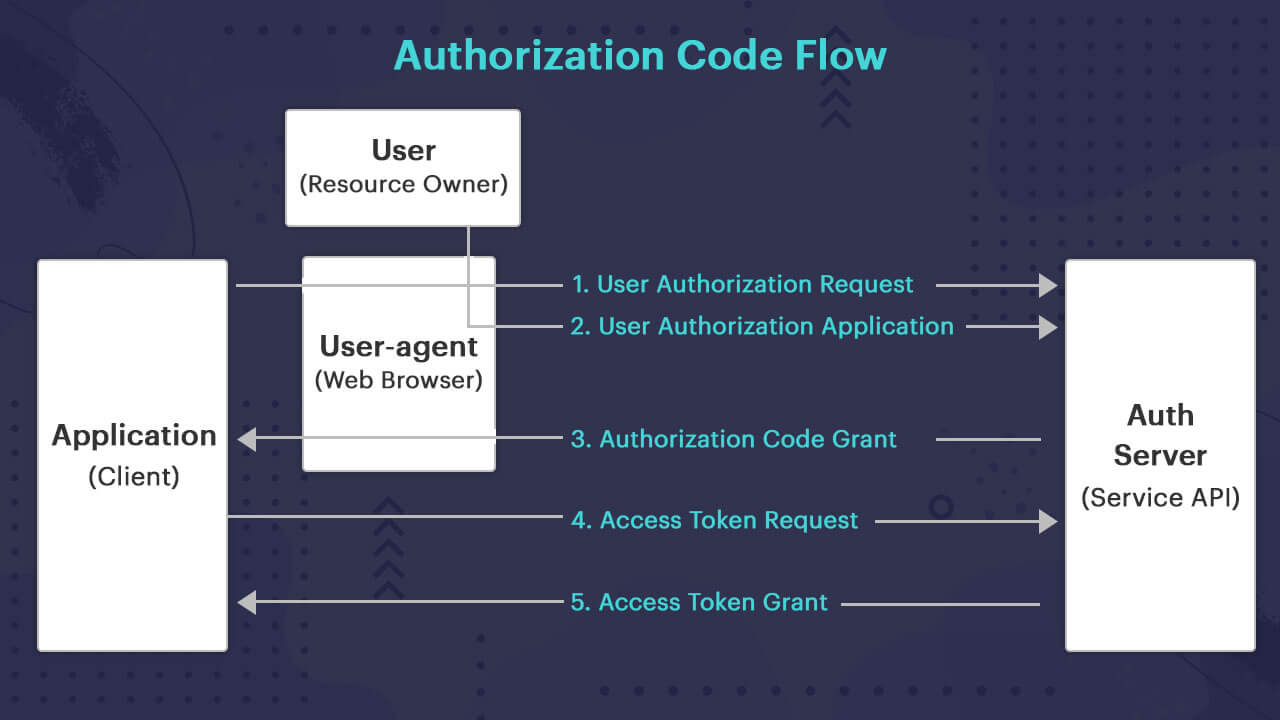
Whether you use a readymade API or build your own, it is important that you keep the security measures in check. It is always an important component for developers. Moreover, it is crucial for mobile development. Developers have to access control mechanisms, privacy control, and secret keys before invoking web-based APIs. There was a time when APIs had their own security. However, today, there are API standards like OAuth2, TLS, and Open ID to make the API integration simpler.
Further reading on APIs → API for Mobile Apps Guide
Mobile App Frontend Development
Mobile App Frontend is what your users will see. Mobile frontend development includes a mixed bag of technologies. Some applications require APIs and backends, while others only need to work only with local databases offered by the platform.
Almost all web programming languages can be used to build the backend of your mobile application. If you are building native applications, you can use technology-specific offerings. For example, iOS applications can be developed using Objective-C, Swift Programming Language, Flutter, or React Native. Android Applications can be developed using Java, Kotlin, Flutter, or React Native.
Every programming language offers its own unique capabilities with your desired platform. You should be able to choose a team that understands which necessary technologies can be leveraged the most by choosing the perfect programming language.
Further reading → Mobile Frontend Development Guide
Testing the Developed App
After successfully developing an application, it is necessary that the quality of the application is ensured to be on-point. Quality assurance is a crucial phase in the mobile application development process as it determines the reliability, stability, and usability of the developed application. In order to ensure an all-inclusive testing process, there are a number of aspects that need to be addressed by following a complete testing cycle subjective to each application.
Testing can be broadly classified into two categories, manual testing, and automated testing. It depends on the type of application whether it needs manual testing or automated testing can give accurate results.
Any application must pass through a myriad of testing methods to come up with a perfect application. Some of the major testing methods that are a must-do for all the mobile applications are,
Functional Testing
With this testing method, you can check whether your application is behaving as it should justify all the specifications. Functionality testing is an important part as each user will behave differently and use the app in a different way. So, you need to make sure that the app functions as desired for all the possible test cases. Functional testing includes,Installation & initialization of the application on all the distribution channels
Business features and functionality testing
Testing fields, parameters, and user feedback fields
Testing any possible interruptions
Testing necessary device resources
Testing possible updates for each distribution channel
Further reading → Guide to Functional Testing
Performance Testing
The application that you have developed should serve its purpose by giving the performance that it is designed for. Moreover, with performance testing, one can check the consistency in performance when the load varies or there are any exceptions. It includes,Volume testing to check the app’s performance under a high volume of data
Load testing to check the speed of the app when subjected to normal and extreme load
Stability testing to see whether the app behaves normally under all conditions
Testing the response time of your application in all conditions
Concurrency testing to see whether the app’s performance changes if multiple users are logged in
Testing the battery usage of the application to ensure there’s no battery drain or memory leak.
Further reading → Performance Testing Guide
User Experience & Interface Testing
It is necessary to ensure that the UI/UX is as per the client’s needs and specifications. Also, the user interface is such that the users find it easy to use and accessible. The0 main aim of this testing is to check whether the final implementation matches the envisioned or proposed design. It includes,Testing flows, visual interaction, and ease of navigation
Checking on the consistency in design, fonts, icons, etc. across the application
Interface testing to ensure that the color scheme, design, and entire look is in synergy with the theme of the application
Testing the interaction speed and navigation ambiguity
Ensuring that the design guidelines are strictly followed in the final design of the application
Further Reading → UI Testing Guidelines
Documentation Testing
The mobile application development process is embarked on the creation of a document that mentions the requirements, screen layouts, specifications, and client needs. Hence, if there is any mismatch between the document that is prepared and the developed application then it can be a big thing to ponder upon. Documentation testing includes,Creation of test cases, requirements, and testing plans
Analysis of the test cases, and plans
Testing for any discrepancies in the documentation
Creation and analysis of navigation flow, screen layouts, etc.
Checking the wholeness of the design and resemblance with the requirements mentioned in the documentation
Further Reading → Documentation Testing
Security Testing
Security is a major concern when you are developing an application as even a minor mistake can lead to major vulnerabilities to data leaks. The major aspects covered in security testing are checking for any risk to sensitive data, threats from hackers, etc. Security testing is done in many ways which include,Threat analysis and testing for authentication of login credentials
Vulnerability analysis to check for any loopholes in the application
Testing for the proper platform and secure server-side controls
Checking for any potential aspects that hackers could possibly attack
Testing for any potential threats from any permissions to be given to applications
Further Reading → Security Testing Guidelines
Configuration Testing
The application that is developed needs to be completely compatible with whatever device it is designed for and the configuration needs to be checked beforehand. In configuration testing, the actual performance of the application is checked on various devices and detects any missing features. Configuration testing comprises of,Testing device configuration for all the devices
Checking browser configuration and compatibility
Ensuring secure database configuration
Testing network connectivity and configuration
Checking for operating system configuration for all the devices
Platform Testing
With new devices coming in the market daily, and each one with different hardware and features, it becomes inevitable for the mobile application development process to include platform testing. The aspects covered under platform testing are,Testing platform compatibility for different operating systems, and client-side browsers
Mobile application testing on various devices to ensure device compatibility across multiple devices
In the case of cross-platform mobile applications, platform testing is done for checking compatibility with each of the platforms
Checking for cross-browser compatibility of the mobile application that is developed
Recovery Testing
The ability of your mobile application to recover from any kind of error or failure. The application may face any kind of failure, whether it is hardware or software, or even any issues in the communication of the app with the device. So, it becomes important to conduct recovery testing before deploying an application. It includes,Testing the application’s failure mechanisms in case of software issues
Checking the response time and methods when the hardware misbehaves or fails
Testing the lagging or checking the response time if communication is lost and how recovery is done
Checking the recovery time and ways in case of any of the above failures encountered by the application
Beta Testing
Once the application is ready and passes almost all the tests, then it is time for the application to be tested by real users. This testing is known as beta testing. Beta testing is a holistic approach to test the overall performance in terms of reliability, security, functionality, and compatibility. It includes,Testing the application with a number of users for checking the reliability and behavior of the application
Checking the response time of the application for the different test users.
Testing the application for users over a large demographic coverage for any loopholes
Testing the application for any misbehavior in case of any in-app purchases or any application cost
Certification Testing
In order to check whether the application meets the standards of various play stores and app stores, it is necessary to conduct certification testing. This testing is the final and important testing step and it includes,Checking the licensing agreements of Google Playstore, Apple App Store, etc.Testing whether the application development follows all the terms of use of the various app stores
Checking for any violations of the terms and conditions stated by the play store, app stores, etc.
Testing Phases
Being a crucial part of the mobile application development process, the testing phase is made up of different steps to measure the quality of the developed application. Here’s a step-by-step guide to the complete mobile application development testing process.
Test Scope
This is the first and most important step of the testing process in which you define the parameters, features, or functionalities that you are going to test. Whether you want to test only a few functionalities or carry out testing of the entire mobile application. In the mobile application development process, once the scope of testing is narrowed down, then it can be easier to determine which test methods need to be deployed. Whether the mobile application requires only functional testing, performance testing, security testing, or it requires a mix of various testing methods.
Parameters to consider while defining the scope of testing:Type of app: Native or Hybrid
Is the app interacting with other apps?
The necessity of network compatibility testing
Front-end testing, back-end testing or both
Checking Device, operating system, and version coverage
Deciding on the coverage of locations for testing
Planning
Once the test scope is clear, it’s time for the creation of a plan to move forward. In this planning stage, you are finalizing the strategy of testing by categorizing or breakdown the entire process into chunks for ease. When you are creating the plan of action, the first thing you will stumble upon is the choice between manual testing or automated testing. Another thing that comes in this stage is the creation of test cases and scripts in case an automated testing method is chosen. Things included in the planning stage are,Identifying the testing methodology that matches the mobile application requirements
Writing and choosing test cases tailored to the mobile application that is developed
Choosing whether testing is to be done in-house manually or use of any software
Selecting the testers if you are not doing it in-house is quite important
Execution
After defining the scope of testing and planning the strategy, writing test cases, and settling upon the methods of testing, it’s time for executing the entire testing process. The execution phase can be successfully carried out only if the scope and testing methodologies are clearly defined. Testing execution focuses on the specifications of the devices, platforms, or operating systems on which the application is to be tested. Again, there are a few things that need consideration,Execution of various testing methodologies depending on the scope and priority
Identifying the areas of improvement and resetting the testing goals
Sending test results periodically in order to deploy changes asap
Continuously testing right from the development stage to the deployment stage
Tracking
Once the testing process is executed, it’s now time for analyzing and logging in the results and errors. When you are tracking the results of testing, the first thing you need to do is prioritize the results based on their severity and need for immediate corrective action. Highly non-negotiable and risky defects need to be addressed first. There is much software that can be used for tracking testing results. The major factors important in tracking test results are,The decision of prioritization of the defects: Low, Medium, High, or Blocker
Resolution of defects based on priority and not avoiding even the simplest defect such as a spelling mistake
Logging defects in order to make sure that they are corrected in time
Choice of a reliable partner for tracking testing results
Review
Once the test run is completed and all the defects are either corrected or logged it is time for the review process. In the review process, you need to create a summarized report of the entire testing process and then review it in order to get a better understanding of the errors and behavior of the mobile application. The documentation should include even the simplest or lowest priority detail and not missing out on anything. Things to be included in the review document:Details of all the devices, operating systems, and versions on which the mobile application was tested
Complete summary of all the tests conducted along with results
Total number of tests conducted with relevant software used and results
A final word on whether the mobile application is ready to hit the market or needs more improvement
Deployment and Maintenance
Once you have built and tested the mobile application, it is time to deploy it, and maintain it for further development.
Mobile App Deployment
Mobile app deployment is also known as mobile app launch. Deploying mobile applications can be a tiring task, especially if the application is multifaceted, and required lots of testing. Here’s a short guide to help you launch.Make sure it passes all the deployment tests. If you write an end-to-end unit and integration tests, make sure to check their output. Make them work anyhow.
Rebuild your application – Sometimes when obfuscating code on Android, developers use ProGuard, which can sometimes remove code, leading to app crash. Make sure you don’t shrink the code at the cost of usability.
If you already own a server, set up your CI flow using Jerkins, Bitrise, CircleCI, Travis, or Bitbucket Pipelines.
It is also essential that you perform static code analysis using Lint, ktlint, pmd, checkstyle, findbugs, detekt, gradle-static-analysis-plugin, OCLint, tailor, Swiftlint, Clang Static Analyzer, Infer, Swift Format, Swimat, or FauxPas.
Prepare a product version of your mobile app and release it for internal testing. Try to use crash reporting tools like Instabug or Fabric.
Preparing builds can be automated as well. For example, tools like Fastlane can help you automate screenshots, beta deployment, App Store / Google Play deployment, and code signing.
Monitoring engagement will help you discover user insights. You can integrate tools like Google Analytics, Fabric, Amazon Pinpoint, Mixpanel to discover active users, session intervals, time spent using the app, ScreenFlow, retention, conversion, and lifetime value.
Further reading – mobile app launch checklist
Best Practices for Mobile App Deployment
Once the user installs the application, you should work on minimizing uninstalls, deliver the best user experience, keep up with the competition, and achieve maximum financial benefits in the long run. Regularly maintaining your mobile application to create a sustainable brand image in the minds of the users. Here’s a list of best practices for long-term app development.
#1 Monitor the performance of your mobile application. Keep an eye on loading types, if there are any lags, or if there are any responsiveness issues. This will help you stay ready with your analytics report. Analyze your retention rates, churn rates, and try to understand usage patterns.
#2 Keeping your user interface updated is also one of the ways to maintain your mobile application. Customers align themselves with changing styles, trends, habits, and other essential features of the apps that need constant updating. If you keep your app interface the same, your customers might gradually start preferring other competing apps with similar features.
#3 Ensure that your app supports the latest software updates and hardware updates. A new version of the mobile operating systems is released every year. Think about how many mobile devices can be upgraded to the latest version of that os, and thus your app?
#4 Fixing bugs can win customers. No software application is ever published with proper testing. However, bugs are an integral part of mobile app development. Fixing bugs can display your faith and dedication towards your users and also towards your mobile phones.
#5 Regularly add new features to your app. You can do this by observing how users are interacting with your app. With the help of insights received, you can discover what’s working for your user, and what isn’t.

0 Comments